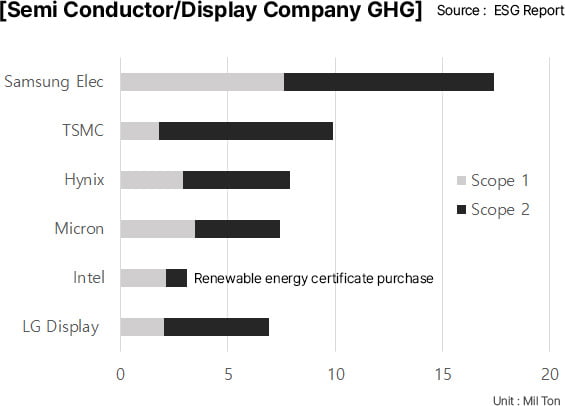
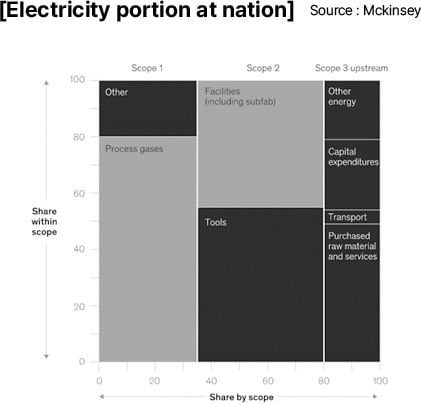
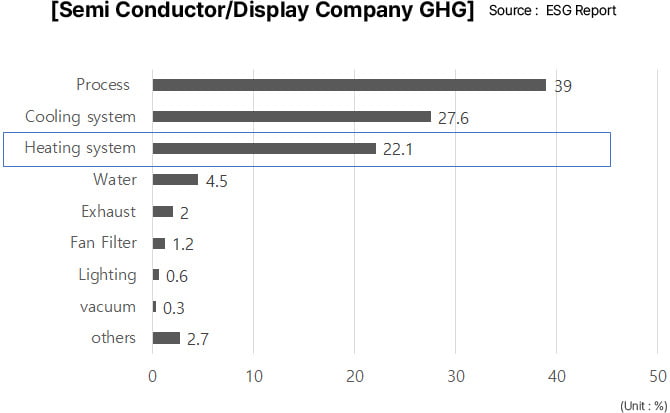
ESG
WW Energy Consumption by Source
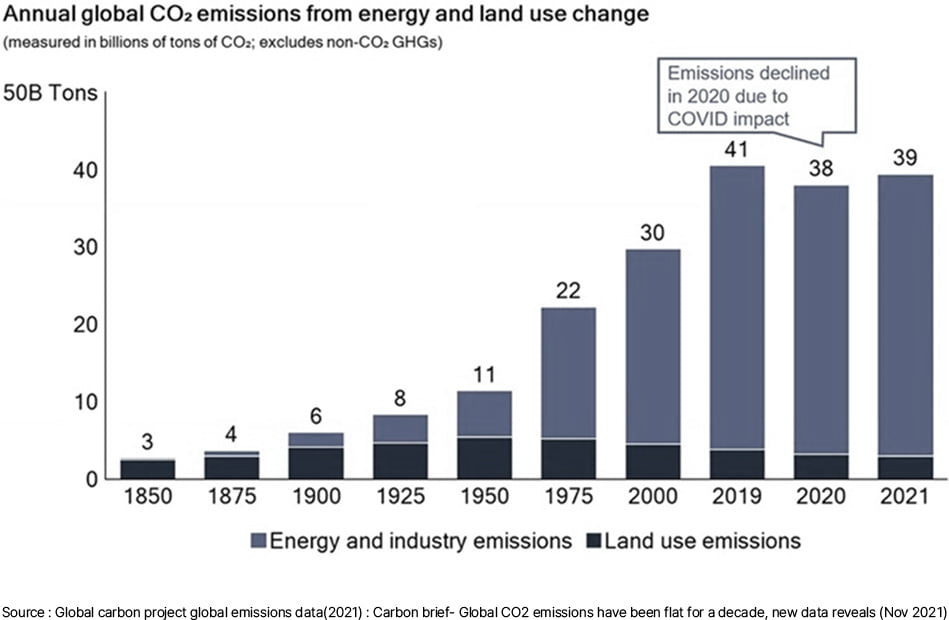
World energy consumption never stops, keeps growing. Fossil fuel has been the major source (83%) in world energy consumption
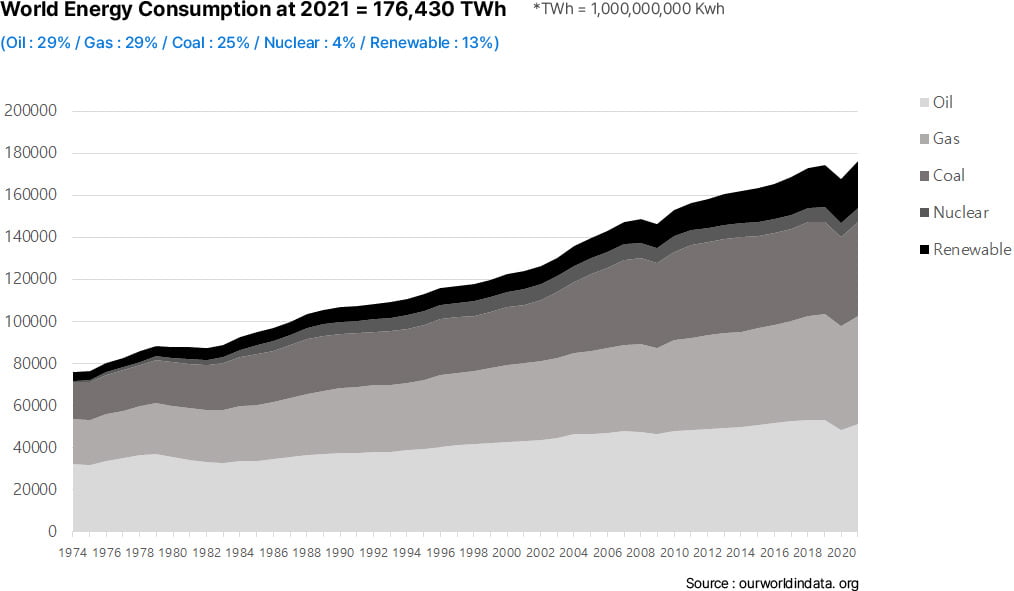
World energy consumption decreases only at disaster like Covid or Lehman Incident.